
Now, Servo motors will accept PWM command and hence we need to attach servo data pin to the PWM pin of Arduino. To capture the analog output of the Joystick, we can connect the X and Y axis pin of the joystick to the analog pins. Interfacing Joystick and Servo Motor with ArduinoĪs we studied earlier, Joystick will give analog output. Now, we need to interface both of the peripherals with the development board. We studied about Joystick and Servo motor, now we will move further to control the servo motor with Joystick. Otherwise, It may not able to get proper signals from the board. While powering servo externally, make sure you connect GROUNDS of External power source and board. Hence, make sure that you are providing an external power source to the servo motor. In fact, Servo will not get enough current from Arduino Board and it will not work. The same will apply for Servo Motor as well. Personally, I will recommend keeping a separate power source for external peripherals.


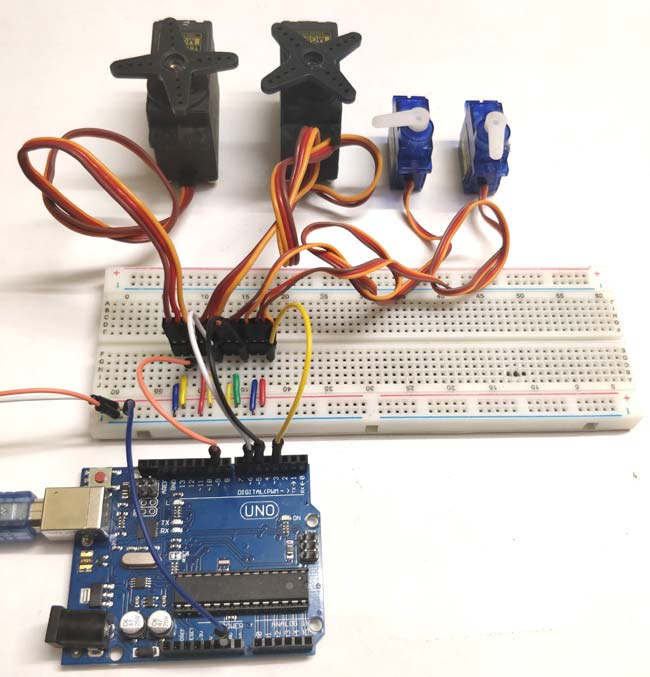
Two for power source and one is data pin. It gets pressed when you press the shaft. We will learn more about these axes later in this tutorial. The next two pins are for X-Axis and Y-axis. The first two pins are Ground and Vcc respectively, where we need to apply a voltage between 3.7v to 6v. Joystick PinoutĪs shown in the figure below, Joystick has 5 pins. Before going further, let’s have a look at the pinout of a standard Joystick. As we know the basics of potentiometers, a joystick simply consists of two potentiometers aligned on X-Axis and Y-Axis. The joystick is a small input device, which can pivots on its base easily. So, let’s learn to control the servo motor with Joystick! A short note on Joystick We will also study the program for the same. Before going to understand connections and programming, we will take a brief look at Joystick and servo motor to refresh the basics. We will control two servo motors with the help of Analog Joystick.

In this tutorial, I will be demonstrating, how we can control servo motors with thumb Joystick and Arduino.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
